These vegetarian lunches are great for quick snacks or healthy meals. These recipes are easy to prepare and can also be prepared cold or hot. Some recipes can be frozen and prepared quickly for your lunchbox. These ideas are perfect for lunchboxes, and they can be customized to meet your needs.
A lentil salad is a healthy and filling vegetarian option for lunch. This vegetarian entree is made using lentils, veggies, and feta. This recipe is easy to prepare ahead of time. This recipe includes drained canned lentils, which are a good option if you are short on time. To make this a hearty dish, you can use quinoa in place of lentils. This lentil salad is great for lunchboxes as it comes with a homemade garlicky peanut dressing. You can also eat this salad at room temperatures.
A smashed white bean salad with avocado is also available. This vegan salad is loaded with nutrients and packed full of umami flavor. This salad is delicious with pita chips or crackers. This salad can also be eaten any time. It can be dressed with a lemon-tahini sauce.

Another great lunch option is a vegan banh mi. The sandwich can be made in a matter of minutes and will last for several days in the fridge. A lunchbox is also an option if you're short on time. While this sandwich takes a few ingredients, it's very easy to assemble at home.
Another vegetarian option is a grain bowl. This recipe has a variety vegetables, grains, herbs, and spices. This recipe can be prepared in advance and is great for those who are busy. This salad can be eaten hot or cold. This salad is easy to prepare and can be customized with your favorite vegetables. This recipe can be prepared up to 5 days in advance.
Hummus Bowls are another excellent vegetarian lunch option. It is quick and easy to make, and the flavors taste great. For those who enjoy Oriental-style cooking, this recipe is ideal. This recipe is also packed with protein. It can be served either as a main meal or as an accompaniment. The hummus is spread over the top, and optional pre-cooked rice can be added.
You can also make the Veggie Cream Cheese. This homemade spread is ideal for dipping vegetables or crackers. You can enjoy it with pita chips or gluten-free crackers. It's also great to freeze for a quick lunchbox snack. This dip is great for dipping pretzels. It's a nutritious snack that can be enjoyed anytime.
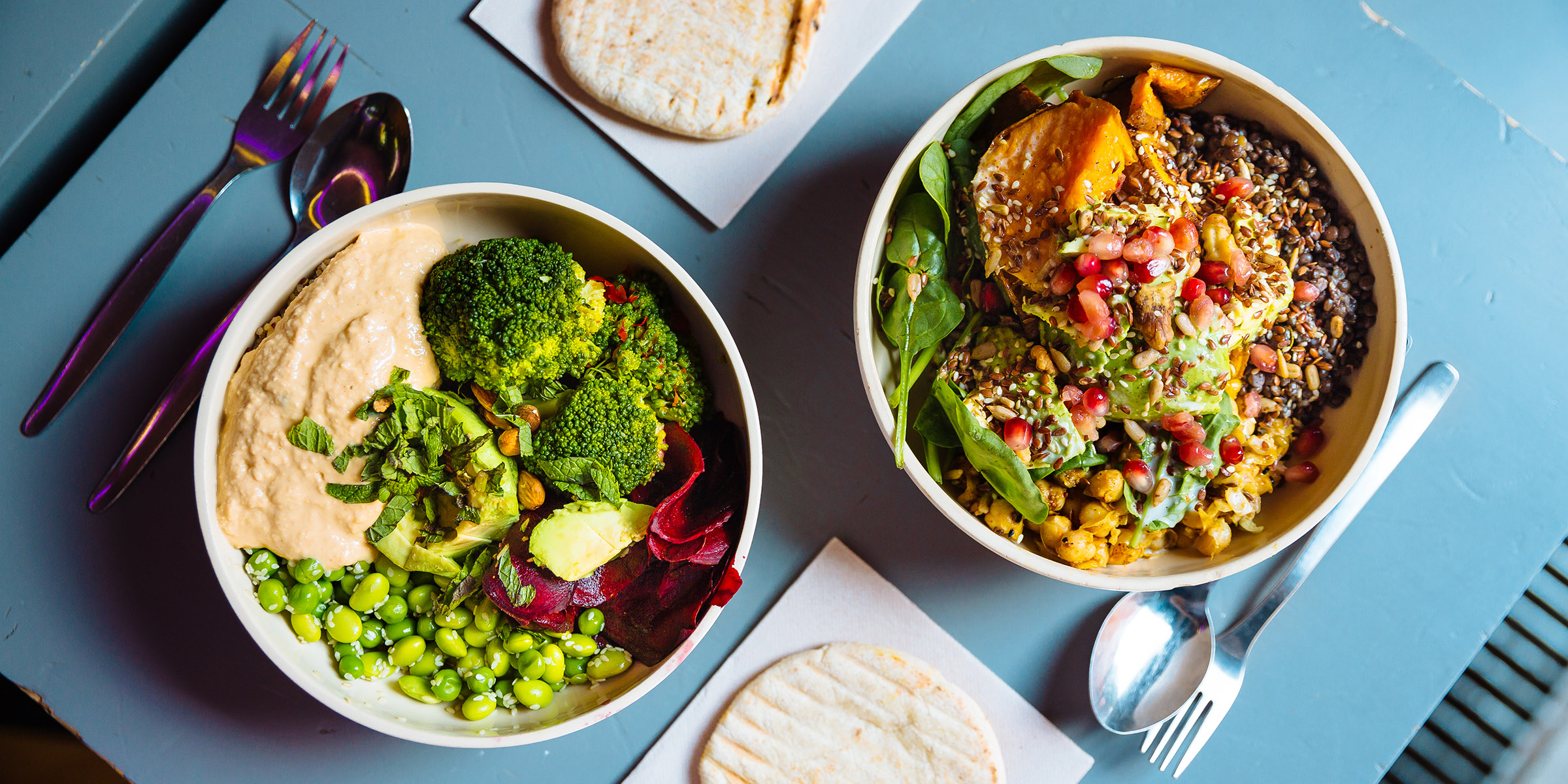

A lentil salad is another great option for a vegetarian lunch. This is a delicious meal that can be served with pita chips or crudites. It is also possible to make a quick soup with turmeric lentils. The recipe has hearty grains, kale and vegetables. This recipe can be prepared ahead of time, and is a healthy, tasty lunch option.
FAQ
Here are 7 ways to live a healthy lifestyle.
-
Be healthy
-
Exercise regularly
-
Sleep well
-
Drink plenty of water.
-
Get enough sleep
-
Happy!
-
Smile often
Exercise: Good or Bad for Immunity?
Your immune system is strengthened by exercise. Your body makes white blood cells that fight infections when you exercise. You also eliminate toxins. Exercise is a great way to prevent diseases such as cancer and heart disease. It can also lower stress levels.
But too much exercise can damage your immune system. Exercising too hard can make your muscles sore. This can cause inflammation, swelling, and even death. Your body then has to produce more antibodies to fight off infection. However, these antibodies can also cause allergic reactions and autoimmune diseases.
So, don't overdo it!
What can you do if your immune system is weak?
The human body is composed of trillions if not billions of cells. These cells work together to form organs and tissues that perform specific functions. Another cell takes its place when a cell dies. The chemical signals known as hormones are used to communicate between cells. Hormones regulate all bodily functions from growth and developmental to metabolism and immunity.
Hormones are chemical substances that glands secrete throughout the body. They circulate through the bloodstream and act as messengers to regulate how our bodies function. Some hormones come from the body and others are produced outside.
Hormone production starts when hormone-producing cells release their contents into your bloodstream. Once released, hormones move through the body until they reach their target organ. Some hormones are only active for a brief time. Other hormones stay active longer and continue to influence the body's functioning even after they leave the bloodstream.
Some hormones may be produced in large numbers. Some hormones are produced in large quantities.
Some hormones only are produced during certain periods of life. The production of estrogen can occur during puberty and pregnancy, as well as menopause and old age. Estrogen helps women develop breasts, maintain bone density, and prevent osteoporosis. It helps to stimulate hair growth and maintains skin's softness.
How can I tell what is good for me?
You need to listen to your body. Your body is the best judge of how much exercise, food and rest you should get. It's important to pay attention to your body so you don't overdo things. Take care of yourself and listen to your body.
Statistics
- WHO recommends consuming less than 5% of total energy intake for additional health benefits. (who.int)
- The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend keeping added sugar intake below 10% of your daily calorie intake, while the World Health Organization recommends slashing added sugars to 5% or less of your daily calories for optimal health (59Trusted (healthline.com)
- nutrients.[17]X Research sourceWhole grains to try include: 100% whole wheat pasta and bread, brown rice, whole grain oats, farro, millet, quinoa, and barley. (wikihow.com)
- In both adults and children, the intake of free sugars should be reduced to less than 10% of total energy intake. (who.int)
External Links
How To
What does the term "vitamins" mean?
Vitamins are organic substances found naturally in food. Vitamins help us absorb nutrients in the foods we consume. Vitamins cannot be made by the body; they must be taken from food.
There are two types if vitamins: water soluble, and fat soluble. Water soluble vitamins dissolve easily in water. These include vitamin C (thiamine), Vitamin B1 (riboflavin), Vitamin B2 (riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (niacin), Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), Vitamin C, B1 (thiamine), Vitamin B2 (riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (niacin), and Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine). The liver and fat soluble vitamins are stored in fatty tissue. You can find vitamin D, E K, A and beta carotene as examples.
Vitamins are classified according to their biological activity. There are eight major vitamin groups:
-
A – Essential for normal growth, and the maintenance of good health.
-
C - important for proper nerve function and energy production.
-
D – Essential for healthy teeth, bones and joints
-
E is needed for good reproduction and vision.
-
K - required for healthy muscles and nerves.
-
P - Vital for strong bones and teeth.
-
Q - aids in digestion of iron and iron absorption
-
R - necessary for making red blood cells.
The recommended daily allowance (RDA), for vitamins, varies based on gender, age, and physical condition. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets the RDA values.
For adults aged 19 or older, the RDA of vitamin A is 400mg per day. Pregnant mothers need 600 micrograms a day to ensure fetal growth. Children ages 1-8 require 900 micrograms per day. Babies under one-year old need 700 micrograms per daily. Between 9 and 12 month, however, this drops to 500 mg per day.
Children between the ages of 1-18 need 800 micrograms per daily for obesity, while those overweight require 1000 micrograms. To meet their nutritional needs, children underweight and obese need 1200micrograms.
Children aged 4-8 years old who have been diagnosed as having anemia require 2200 micrograms of vitamin C per day.
2000 micrograms is the minimum daily intake for general health in adults older than 50 years. Due to their increased nutrient needs, pregnant and breastfeeding women need 3000 micrograms daily.
Adults over 70 years of age need 1500 micrograms per day since they lose about 10% of their muscle mass each decade.
Women who have been pregnant or are lactating require more than the RDA. Pregnant and breastfeeding women require 4000 micrograms each day during pregnancy and 2500 Micrograms each day after birth. Breastfeeding mothers need 5000 mg per day when breastmilk is being produced.